How to Increase Website Speed and Get a Lightning Fast Website in 2021
When it comes to a website’s performance, speed is of the utmost importance.
To reduce your bounce rates and increase visitors’ engagement, it’s fundamental to have a fast-loading website.
A site that is optimized for speed not only enhances the user experience (UX) but can also help to boost your search engine rankings.
Therefore, you need to understand how the metrics work, what influences them, and how to improve them in order to take your website at the top performance.
What is Website Speed?
Website speed is a measurement of how fast your website loads. It is actually the page speed for a sample of page views. Whereas, page speed shows how fast the content on your page loads. You can describe it as either:
- Page load time – the time it takes to fully display the content on a specific page.
- Time to first byte (TTFB) – how long it takes for your browser to receive the first byte of information from the webserver.
Why is Website Speed Important?
Website speed is highly related to the success of your website as it can influence page views, user experience, conversions, search ranking, and many more.
As mentioned in Google Study, a slow-loading website makes people abandon it. Especially on mobile, the slower your site, the more likely it increases the bounce rates.
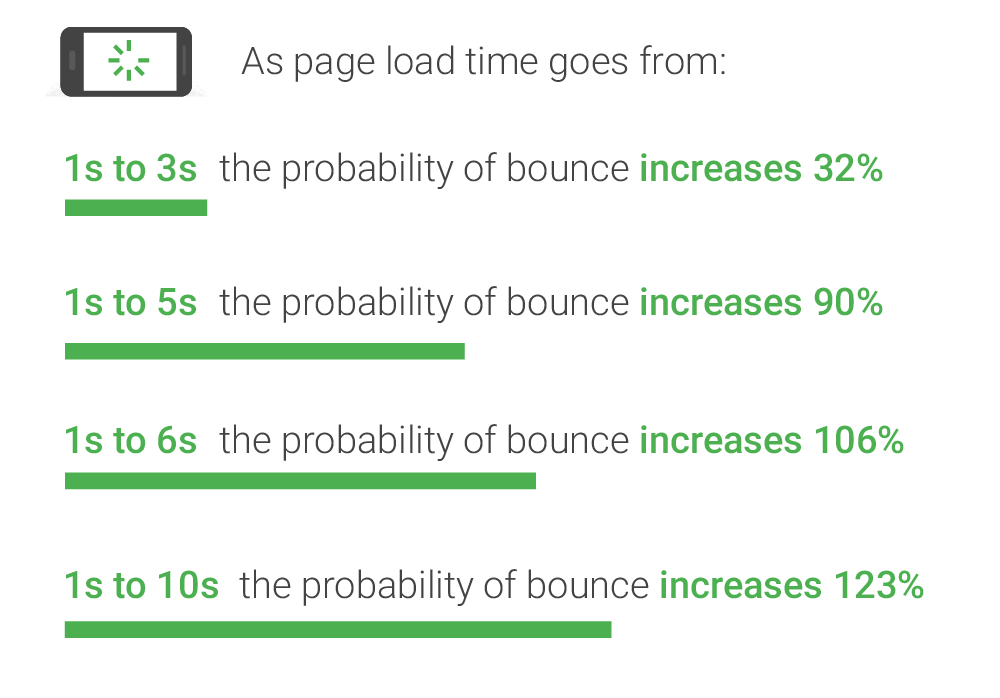
For more details, here are the reasons why website speed matters:
Website speed is the first impression to your visitors
When someone clicks on your website, the first thing they face is the loading page. If your website loads fast, it will give good impressions like “WOW this website is fast, they must be professionals”. Then, they can happily read through your website.
Not only that, but this speed thingy is also highly related to impressions like efficiency, trust, and confidence. Giving a good user experience at the first click on your website is important!
Everyone wants a fast-loading website!
Everyone is looking for quick answers and immediate results on the internet. Apparently, most people expect a website to load not more than 2-3 seconds. If it takes longer, they will just abandon it and move on to another website. Therefore, it’s best to have a speedy website.
Give a good user experience
One of the biggest factors contributing to a user experience is providing information fastly. That’s why website load speed is the number one priority when it comes to good user experience. People visiting your website are looking for something. Give it to them as quickly as possible.
It affects your page ranking on search engine
All search engines, including Google, take the loading speed into account when ranking websites. When you have a slow website it may drop your ranking on search engines. Moreover, Google once said that they will reduce the number of crawlers it sends to your site if your server is slower than two seconds.”
That means Google is less likely to pick up your latest blog post or notice any other recent updates. Therefore, speed is important to maintain for a website!
It reduces conversion rates
A slow website means driving people away. Of course, it is driving your sales away too. Amazon did a test that showed slowing down one second on the website make them lose $1.6 billion every year. Pretty big deals, right?
How to Measure Your Website Speed?
Website speed tests assess how your website is performing. You need to run a speed test regularly to track performance and see whether your website’s downgrades or improves. Through a speed test, you can identify which areas slow down your website and find out how to improve them.
There are many free website speed testing tools that provide a high-quality speed test. For instance, Pingdom, GTmetrix, Google Page Speed Insights, and many more. You can find out more about the Best Website Speed Testing Tools to Assess Your Website in 2021.
Tips to Increase Website Speed
Move Your Website to A Better Host
Your website server plays a big part in the time to first byte and how fast your website loads in general. Before choosing which server is right for you, you need to take a look at types of hosting out there:
- Shared — It is a shared server with many other websites, all competing for the same resources like CPU power, RAM, etc.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) — It is similar to shared hosting but with fewer other sites on the same machine and everyone gets their own dedicated processing resources without the possibility to exceed them.
- Dedicated — You can have your own server all by yourself, plus control over its setup, hardware, and much more. However, this needs technical skills to handle it or money to hire someone who has them.
- Cloud — It uses a pay-as-you-use model: you get access to as much or as little processing power as you need. Very good for traffic spikes but also pricier.
- Managed — This hosting is taken care of by the provider including security, backups, performance, etc. So, you can focus on building your website content only as the technical things have been taken care of.
From these options, you can choose which server hosting suits you. Other than that, it’s better to pick a hosting provider who has a data center near where most of your audience resides.
Read more: Top 10 Best Web Hosting in 2021
Leverage CDN (Content Delivery Network)
If you want to massively reduce speed problems like latency and locations then you should start to use CDN.
A content delivery network (CDN) is a set of web servers distributed across various geographical locations that provide web content to end-users with regard to their location. This will boost your website’s speed as it caches content in multiple locations around the world closer to where your visitors are at. Making them able to experience faster page loading time on your website.
Compress & Optimize Your Images
Generally, you should try to keep page weight as small as possible. According to Google, the best practice is to stay under 500KB to obtain a fast page loading time.
Images take up a large percentage of Internet traffic and they often take the longest to load on a website since image files tend to be larger in size than HTML and CSS files. Therefore, you need to reduce the load time by image optimization. Optimizing images involve reducing the resolution, compressing the files, and reducing their dimensions. There are many image optimizers and image compressors available for free, such as Caesium Image Compressor, WP Smush Plugin, and many more.
Read more: Top 10 Best Image Compressor Tools to Boost Your Website SEO Ranking
Perform Caching
Caching is one of the most effective ways to speed up your web pages. Caching stores copies of your site’s files, minimizing the work needed for the server to generate and serve a web page to a visitor’s browser. It can help to decrease Time to First Byte (TTFB), by requiring the server to use fewer resources to load a page.
There are a few forms of caching:
- Browser caching — Tells browsers to store fixed assets like style sheets or JavaScript files on the local hard drive. With this, the browser can simply use them from there instead of downloading them again.
- Object caching — Stores queries to the database in the local memory of the server so that it can answer them without actually having to access the database.
- Edge caching — This means saving files on a server closer to the end-user.
You can perform caching using plugins like WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache, LiteSpeed Cache, and many more,
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML code
Optimizing the way your files load can help improve page loading speed. You can achieve that by minifying your CSS, JavaScript, and HTML code. This means removing unnecessary spaces, characters, comments, and other unneeded elements to reduce the size of the files. This makes CSS and JavaScript files slightly smaller so that they load faster in the browser and take up less bandwidth. You can try using minification plugins like Autoptimize or NitroPack.
Use Asynchronous and Defer Loading for Your CSS & JavaScript files
Your site is made up of CSS and JavaScript files. These scripts can load either synchronously or asynchronously:
- Synchronously – files load one at a time, in the order in which they appear on your web page. With this method, when the browser encounters a script, it will stop loading other elements on the page until that file has been fully loaded first.
- Asynchronous – multiple files load at the same time, which can speed up the page’s performance. Setting this up involves eliminating render-blocking resources.
To effectively speed up your website, use the asynchronously loading. This will make the browser keep going down the line without waiting for a file download to be finished. As a consequence, it will load several files at the same time, reducing bottlenecks and loading more quickly.
Reduce Unnecessary Plugins & Fonts
Having too many plugins on your site can cause unnecessary bloat that slows it down. Moreover, plugins that are outdated or aren’t well maintained can pose a security threat, and even introduce compatibility issues that hamper performance. Therefore, you need to reduce them by disabling and deleting any plugins you don’t currently use.
Also, this goes along with fonts. Web fonts have a negative impact on the speed of page rendering. Web fonts add extra HTTP requests to external resources. To avoid this, you can do the following things:
- Use modern formats WOFF2 for modern browsers
- Include only those character sets that are used on the site
- Choose only the needed styles
Reduce HTTP Requests & Redirects
Most webpages will require browsers to make multiple HTTP requests for various assets on the page, including images, scripts, and CSS files. As a result, it will increase the overall load time for a webpage. Therefore, you need to keep the total number of assets to a minimum. You can use website speed testing tools to help you identify which HTTP requests are taking the most time.
This also applies to redirects. Too many redirects on your website can really hurt your loading times. Every time a page redirects somewhere else, it prolongs the HTTP request and response process. Therefore, it is better to avoid using redirects unless it is necessary.
Use Prefetching Techniques
Prefetching requires you to understand your visitors’ behavior on your website first before executing it. Usually, modern browsers allow for prefetching by default as they assume user behavior patterns. This technique loads some content or links in advance to make your load time faster.
There are three main types of prefetching:
- DNS-prefetching – requires resolving domains into IP addresses in advance.
- Link Prefetching – If you are sure that a user will click on a specific link to navigate to some page, you can apply this type of prefetching. The method is useful for stable user journey actions, like moving to the shopping cart page after one or several items were added.
- Prerendering – This approach means rendering an entire page or some elements of it in advance
Implement AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) is a project implemented by Google to help mobile pages load faster. It works by making an open-source format that strips away tons of unnecessary content, making your mobile pages load nearly instantly. As a result, it gives users a more streamlined experience on mobile without any clunky features that don’t work well on mobile devices.
On Google search results, these AMP articles are often relegated to the “Top Stories” and load up instantly. Moreover, it increases the click-through rate from organic search results by 25 percent. You can use plugins like AMP for WP to implement this technique.
Conclusion
Speeding up your website loading time is necessary for you to get on top of search ranking, page views, and conversions. There are many ways to achieve it, starting from running a website speed test to see your website performance on the internet. After that, you can implement the 10 tips on how to increase website speed as mentioned in this article. It includes moving to a better server host, using CDN, asynchronous loading, prefetching, AMP, compressing & optimizing images, performing caching, minifying codes, using asynchronous loading, reducing unnecessary plugins, fonts, HTTP requests, and redirects.




